Git and GitHub
Git: Commands
- Create Repo
git initinitial a folder as a new repo, tracking all modification under it.git/configconfigure only for this repo
git clone <path> [<new dir name>]- cannot create nested repo, so do check your
pwd
- cannot create nested repo, so do check your
git status
- Review Commits
git logfor commit historygit log --onelineshow only 7 characters of SHA and commitgit log --statshow files changed for each commitgit log --patchorgit log -pshow the detailed changes of each commitgit log -wignore the change of blank when showing patch infogit log <7 character of SHA>start from particular commit
git showshow commit with knowing SHA- share all arguments of
git log
- share all arguments of
- Make Commits
git addgit add .to stage all folders and filesgit rm --cached <file>to unstage
git commitopen default editorgit commit -m "commit message"for short commit with only message- Rules of writing commits
- Message: explain the role of submission
- Good: “Update the footer to copyright information”
- no why / no how / no and
- Description: skip a line after message then start
- Message: explain the role of submission
git diffshow changes of unstaged files.gitignorefile under repo to ignore specified files
- Develop on Branches
git tagshow taggit tag -a v1.0 [<SHA>]create a tag “v1.0” with comments (creator / date / message) for (optional) particular commitgit tag -d "v1.0"remove tag “v1.0”- use
git logto verify the location of tag (use--decoratein older version)
git branchshow all branchesgit branch <branch_name> [<SHA>]create a new branch at (optional) particular commitgit branch -d <branch_name>delete branch (inactivate) w/o commit- to delete branch with commits, use
-Dinstead
- to delete branch with commits, use
git checkoutswitchHEADpointer to a branch, making it as active branch- convert file version to latest version of active branch (it replace all files under commit in previous branch, with that in the new branch)
git checkout -b <new_branch_name> <create_on_which_branch>create a new branch and checkout it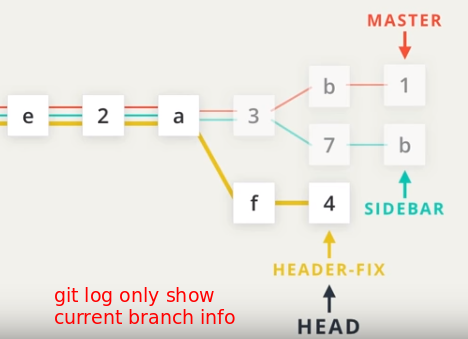
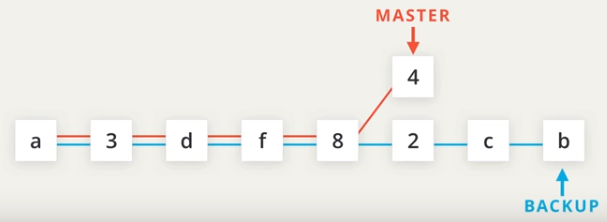
git log --oneline --graph --allshows all branches and commits, also relationshipsgit mergegit merge <other_branch>merge a branch into current branch, likemaster- Fast-forward: moving
HEADto the latest commit (mergesocial-linkstomaster) - Auto-merge: create a commit and merge (merge
sidebartomaster) - Merge conflicts: same row has been differently modified in both branches
- git stop merging and return a single file, combining conflicting portions from both files, showing conflicts with indicators
- update the file and commit it, then merge is completed automatically
- you can just commit it and let merge done, but the conflicts will show in your file
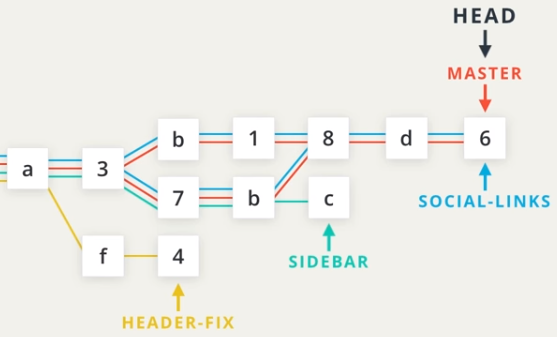
- Fast-forward: moving
git reset --hard HEAD^cancel merge
- Undo Changes
git commit --amendalter the most -recent commitgit addand rungit commit --amendto add new files into last commit
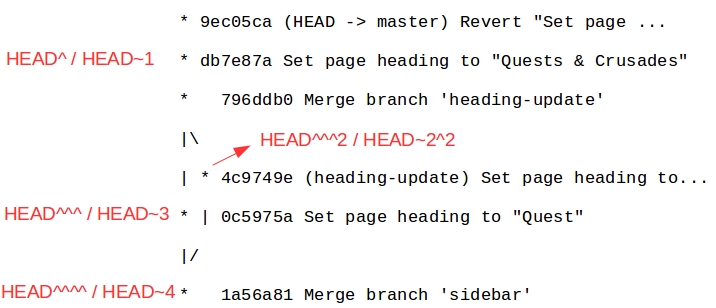
git revert <SHA>create a new commit reversing given commit- Commit Reference
git reseterases commitgit reset --mixed HEAD^^moveHEADback toHEAD^^, and move changes ofHEAD^into working dir (default)git reset --soft HEAD^^move changes back to stagegit reset --hard HEAD^^delete changes- Backup strategy
- before any
resetoperation,git branch backup - after reset, if want to back to the starting point
git checkout -- index.htmlremove uncommited change to file “index.html”git merge backup
- before any
Git: Shell Setting
GitHub: Remote Repo
git remoteshow shortname of remote repogit remote -vshow detailed infogit remote add <shortname> <repo_link>add in repo link and its shortname
git push <remote_shortname> <remote_branch>push all your local git info to remote repo- after
push,git logwill show the commit location of remote-tracking branch
- after
git fetch <remote_shortname> <remote_branch>download remote info and move remote-trackinggit pull <remote_shortname> <remote_branch>fetch and merge with local branch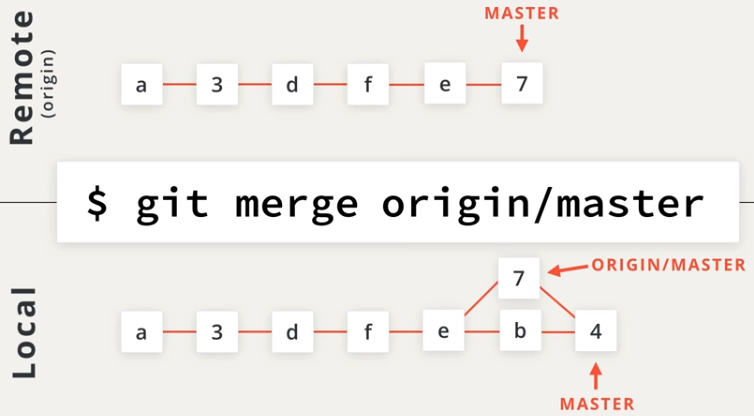
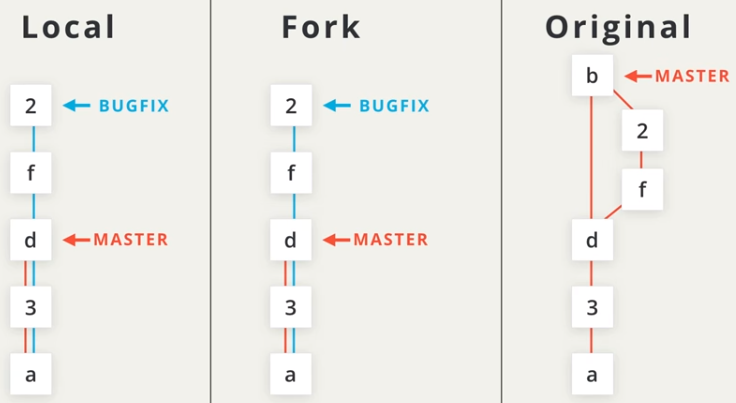
GitHub: Collaborating with Fork
git shortlogshow commits under different collaboratorgit shortlog -s -nshow the number of commits only, sorted by large to small
git log --author="Paul Lewis"show commits made by Paul Lewisgit log --grep="bug"- How to contribute?
Forkthe repo- Check CONTRIBUTION.md
- To contribute large effort, use
Issuesto communicate with project maintenance before starting - Create branch with clear name meeting requirement
- Create clear, frequent and small commits
- Pull request
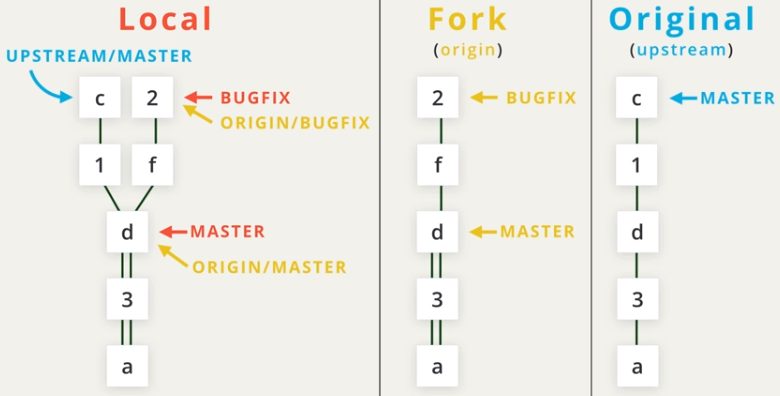
GitHub: Keep Updated to Remote Repo
-
Pull Request
-
Fetch and Pull from Upstream
-
git rebasetransfer commits onto a new basegit rebase -i HEAD~3squash last three commits interactively (refer to YouTube for detailed setting)- need force
git pushdue to deleting commits
- need force
- Backup strategy: create backup branch before
rebase